

The Stirling cycle and Ericsson cycle are two other reversible cycles that use regeneration to obtain isothermal heat transfer. The second law of thermodynamics limits the efficiency and COP for all cyclic devices to levels at or below the Carnot efficiency. For Carnot refrigeration cycles the coefficient of performance for a heat pump is:Īnd for a refrigerator the coefficient of performance is: Where T L is the lowest cycle temperature and T H the highest. The thermal efficiency of a Carnot cycle depends only on the temperatures in Kelvin of the two reservoirs in which heat transfer takes place, and for a power cycle is:

The Carnot cycle is a cycle composed of the totally reversible processes of isentropic compression and expansion and isothermal heat addition and rejection. (Note: 3 of the 4 processes are different) Power cycles normally with internal combustion
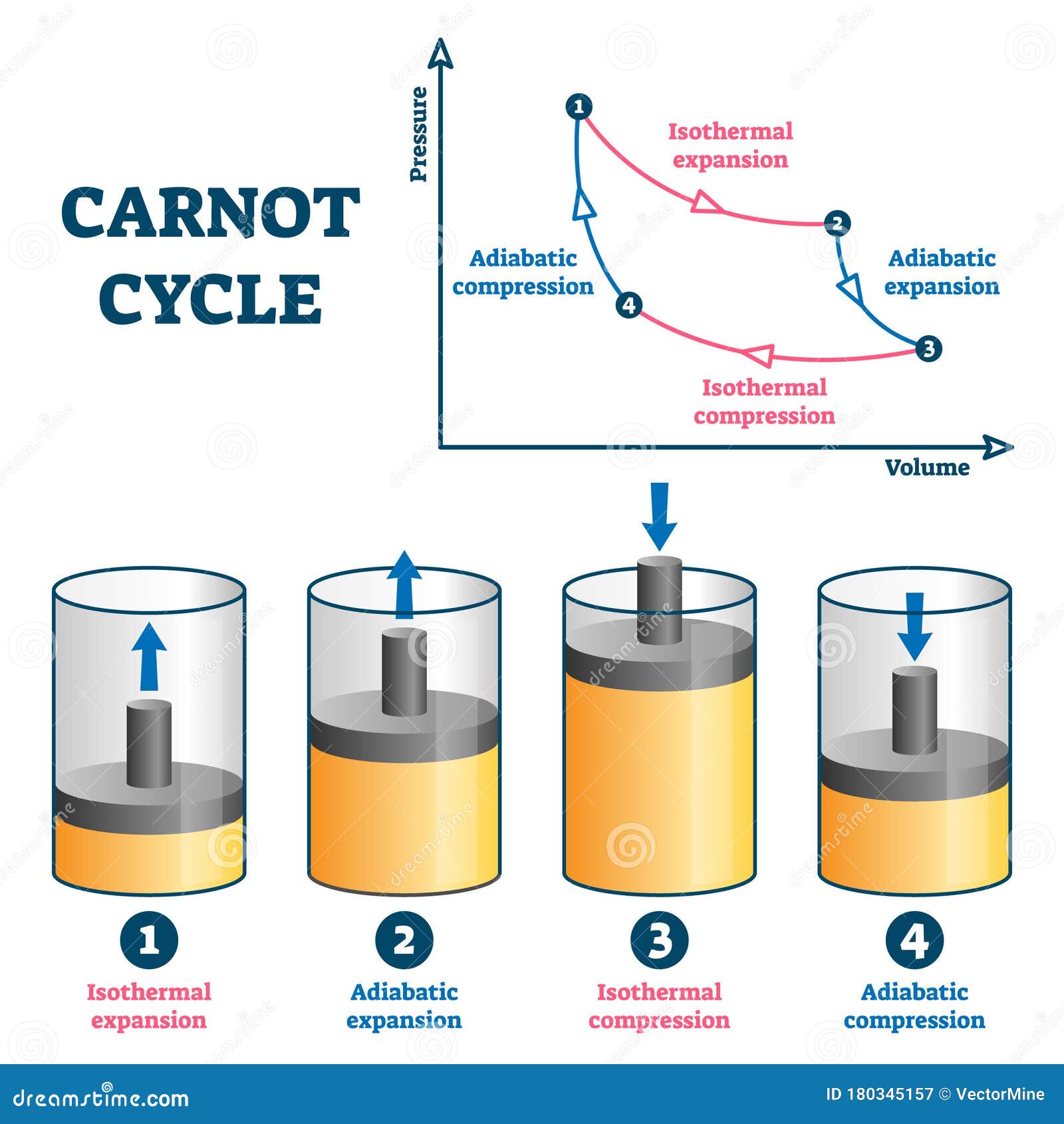
Power cycles normally with external combustion - or heat pump cycles isenthalpic process (the enthalpy is constant).isentropic process, reversible adiabatic process (no heat is added or removed from the working fluid - and the entropy is constant).adiabatic process (no heat is added or removed from the working fluid).isometric / isochoric process (at constant volume).isobaric process (at constant pressure).isothermal process (at constant temperature, maintained with heat added or removed from a heat source or sink).Regeneration in gas refrigeration allows for the liquefaction of gases.Ī thermodynamic cycle can (ideally) be made out of 3 or more thermodynamic processes (typical 4). Gas refrigeration cycles include the reversed Brayton cycle and the Linde-Hampson cycle. The absorption refrigeration cycle is an alternative that absorbs the refrigerant in a liquid solution rather than evaporating it. The most common refrigeration cycle is the vapor compression cycle, which models systems using refrigerants that change phase. The difference between the two is that heat pumps are intended to keep a place warm and refrigerators designed to cool it. Thermodynamic heat pump and refrigeration cycles are the models for heat pumps and refrigerators. Main article: Heat pump and refrigeration cycle If it moves counterclockwise then it represents a heat pump, and W will be negative. If the cyclic process moves clockwise around the loop, then it represents a heat engine, and W will be positive. This work is equal to the balance of heat (Q) transferred into the system:Įquation (2) makes a cyclic process similar to an isothermal process: even though the internal energy changes during the course of the cyclic process, when the cyclic process finishes the system's energy is the same as the energy it had when the process began. The area enclosed by the loop is the work (W) done by the process: A P-V diagrams X axis shows volume (V) and Y axis shows pressure (P). Thermodynamic cycles often use quasistatic processes to model the workings of actual devices.Ī thermodynamic cycle is a closed loop on a P-V diagram. The repeating nature of the process path allows for continuous operation, making the cycle an important concept in thermodynamics.

The first law of thermodynamics dictates that the net heat input is equal to the net work output over any cycle. Variables such as heat and work are not zero over a cycle, but rather are process dependent. Properties depend only on the thermodynamic state and thus do not change over a cycle.
#PCAL THERMODYNAMICS YCAL SERIES#
A thermodynamic cycle is a series of thermodynamic processes which returns a system to its initial state.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
